Breast Cancer Rates Are Rising in Younger Women
In recent years, the incidence of breast cancer has been increasing worldwide, making it a major malignant tumor threatening women's health. We generally classify breast cancer patients who develop the disease before the age of 35-40 as young breast cancer, which accounts for approximately 5%-7% of breast cancer incidence.

The prognosis of young breast cancer is worse than that of breast cancer in other age groups (over 40 years old). This may be due to the unique biological characteristics of the young breast. Young breast cancers often present with larger lesions, poorly differentiated tumor cells, high rates of lymph node vascular metastasis, and molecular subtypes with poor prognosis. These biological characteristics contribute to a larger tumor burden, a higher clinical invasive stage, and a poorer response to treatment. Furthermore, the local recurrence rate in young breast cancer can be 1.5 times that of the general breast cancer population, leading to a higher mortality rate.
The higher incidence of breast cancer in young women is due to factors including genetic factors, hormonal changes, and lifestyle. Specifically:
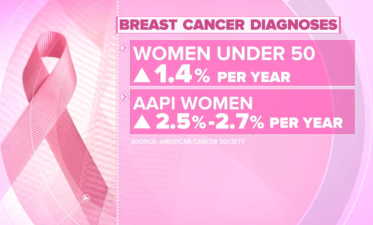
- Genetic factors: Genetic mutations are a significant risk factor for breast cancer, particularly mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. This genetic predisposition may increase the risk of breast cancer in young women in some families. 2. Hormone levels: Fluctuations in women's hormone levels, such as changes in estrogen and progesterone concentrations, are closely linked to the development of breast cancer. Women who take birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy may have an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Lifestyle: Unhealthy habits such as poor diet, lack of exercise, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking may influence the incidence of breast cancer. Obesity is also a significant risk factor, as fat tissue increases estrogen production.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals and radiation may also increase the risk of breast cancer. For example, exposure to high doses of radiation during adolescence may increase the risk of breast cancer later in life.
Young women should monitor their health, undergo regular breast exams, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce their risk of breast cancer.