New Cancer Screening Guidelines for Women Over 40
Cancer screening for middle-aged women should focus on breast, cervical, and ovarian cancers, while other screening tests should be considered based on family history and lifestyle. Annual breast ultrasound is recommended (mammography can be added for those over 40 years old), and cervical TCT and HPV testing should be performed every three years. Other groups, such as long-term smokers, should be screened for lung cancer, and colonoscopy is recommended for those with a family history of colorectal cancer. Cervical Cancer
Risk Factors
① Multiple sexual partners;
② Early sexual activity;
③ Hormone imbalances, etc.
Screening Frequency and Timing
① Women with a sexual history of more than three years or those who are sexually active at age 21 or older can begin cervical screening;
② Under 30 years: Cervical cytology every three years;
③ ≥ 30 years: Cervical cytology every three years;
④ If both the initial cervical cytology and high-risk HPV test results are negative, a combined test can be performed every five years;
Test Items: Cervical cytology (TCT/LCT) or Pap smear and high-risk HPV test;
Breast Cancer
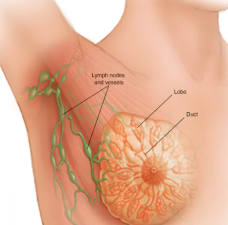
Risk Factors
① Immediate family members (e.g., parents, children, sisters) with a family history of breast cancer
② Women with a history of breast cancer
③ Women who first gave birth to their children over 30 years of age or are not breastfeeding
④ Those who frequently get angry or have breast nodules or hyperplasia that is progressing
Screening Frequency and Timing
General Risk Groups:
① Starting at age 18: Monthly breast self-examination;
② Starting at age 26: +1 clinical breast examination/year;
③ Starting at age 41: +1 breast imaging test/year (e.g., breast ultrasound or mammography preferred);
④ Starting at age 70: +1 imaging test when symptoms or suspicious signs occur;
High-risk groups:
① Starting at age 18: Regular breast self-examination;
② 2-29 years: +1 clinical breast examination (1/6-12 months) +1 breast ultrasound examination/year;
③ 30-75 years: +1 breast ultrasound examination/year (1/6 months) +1 mammogram or breast MRI per year (for those without breast cancer susceptibility genes, 1 mammogram per year after age 50, with additional breast MRI if necessary);
④ Ages 75 and older: Consider a personalized screening plan;
Examination items: Breast ultrasound, mammogram, breast MRI;
Esophageal Cancer
Risk Factors
Age ≥ 45 years and any of the following:
① Long-term residence in an area with a high incidence of esophageal cancer;
② A first-degree relative with a history of esophageal cancer;
③ Presence of esophageal precancerous diseases or lesions;
④ Living and eating habits such as smoking, drinking, and eating hot or spicy foods;
Frequency and Timing of Screenings
① Screening will be terminated from age 45 to age 75 or when life expectancy is less than 5 years.
② High-risk individuals should undergo a checkup every 5 years.
Examination items: Esophageal endoscopy
Gastric cancer
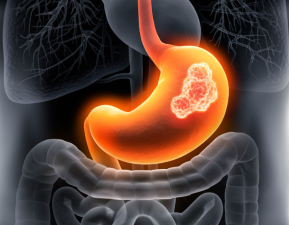
High-risk factors
Most individuals are aged 45 years and above, with the exception of those who have any of the following conditions:
①Long-term residence in a high-incidence area for gastric cancer;
②Helicobacter pylori infection;
③Presence of chronic atrophic gastritis or any of the following precancerous conditions, such as gastric ulcers, gastric polyps, or pernicious anemia;
④A first-degree relative with a history of gastric cancer;
⑤Those who enjoy high-salt, unfresh preserved foods, or are long-term smokers.
Frequency and timing of screenings
Screening should be terminated between the ages of 45 and 75, or if life expectancy is less than 5 years.
According to the new gastric cancer screening scoring system, individuals are divided into high-risk, intermediate-risk, and low-risk groups for gastric cancer. It is recommended that screening be conducted every 1 year or every 2 years, respectively. and every three years.
Examination Items: Esophageal Endoscopy
Liver Cancer
Risk Factors
① Patients with liver disease, such as alcoholic liver disease, fatty liver disease, liver fibrosis, or cirrhosis;
② Patients with chronic hepatitis B or (and) hepatitis C infection and age 40 years or older;
Frequency and Timing of Screening
① Terminate screening between 40 and 74 years of age or if life expectancy is less than 5 years;
② There is no specific age requirement for screening in patients with cirrhosis;
③ Patients with chronic liver disease (including cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, etc.) should undergo monitoring at intervals of 6 months, 12 months, or longer, with 6 months being the most common.
Examination Items: Abdominal Ultrasound + AFP
Lung Cancer
Risk Factors
Patients aged 45 years and older who have the following conditions:
① Those with a long-term smoking history or passive smoking (secondhand smoke);
② Those exposed to industrial pollution or chemical work, or those with pneumoconiosis, tuberculosis, or malnutrition;
③ Those with a direct relative diagnosed with lung cancer;
Screening Frequency and Timing: High-risk individuals aged 50-74 should undergo screening annually;
Test Item: Low-dose spiral CT
Conclusion:
The number of cancer cases is increasing due to environmental pollution, food safety hazards, high stress levels, poor rest, irregular diet, and mood swings. Therefore, in daily life, everyone should balance work and rest. Get enough rest when you need it, avoid staying up late, eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, and undergo regular physical examinations to ensure early detection, treatment, and recovery.