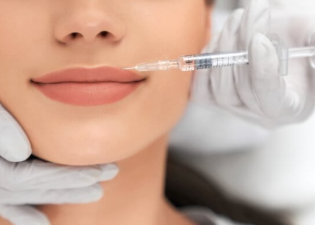
What’s the Difference Between Botox and Xeomin?
Botulinum toxin and chelormin are two completely different concepts, primarily distinguished by their sources, functions, and areas of application.
Botulinum toxin and chelormin are two completely different concepts, primarily distinguished by their sources, functions, and areas of application.
The frequency of botulinum toxin cosmetic injections varies from person to person, depending on individual needs, treatment area, type of botulinum toxin, and brand. Typically, injections are administered every three to four months, but specific circumstances require evaluation and adjustment by a professional physician.
- Treatment Intent: Botulinum toxin injections are commonly used to remove wrinkles, improve expression lines, and lift facial muscles. Different treatment objectives may require different injection frequencies. For example, to remove dynamic lines (such as frown lines), injections are typically administered every three to four months; whereas to improve facial muscle laxity, more frequent injections may be necessary.
- Individual Response: Everyone reacts differently to botulinum toxin. Some may be more sensitive to its effects and require more frequent injections to maintain them; while for others, the effects may last longer and require less frequent injections.
- Treatment Area: Muscles in different areas may absorb and metabolize botulinum toxin at different rates. For example, the muscles around the eyes are relatively small and more sensitive to botulinum toxin, potentially requiring more frequent injections. Muscles in other parts of the face may take longer to show results.
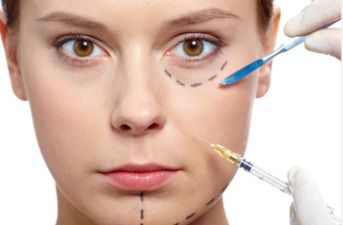
Clostridium botulinum is an anaerobic bacterium that produces a potent toxin, botulinum toxin.
This toxin is one of the most potent known poisons, blocking neuromuscular transmission. It is commonly used in cosmetic surgery as a botulinum toxin injection for wrinkle reduction, face slimming, and leg slimming.
Botulinum toxin works by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, leading to muscle relaxation, thereby improving wrinkles or reducing muscle bulk. The safe use of botulinum toxin requires strict dosage control and must be performed in a professional medical setting.
The concept and function of xeomin
Repair mechanism analysis
- Lipid replenishment
The core of the skin barrier is the lipids between keratinocytes (such as ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids). When the barrier is damaged, using skincare products containing similar ingredients (such as ceramide serum) can directly fill the lipid gaps, repair the "brick wall structure," and reduce moisture loss.
- Enhanced Moisturizing Ability
Natural Moisturizing Factor (NMF) and humectants (such as hyaluronic acid and glycerin) absorb moisture from the environment and maintain the hydration level of the stratum corneum. A moist skin environment promotes enzyme activity, accelerating the repair process of the skin barrier.
- Anti-inflammatory and Soothing
Inflammatory reactions such as redness and stinging can exacerbate skin barrier damage. Products containing ingredients such as Centella asiatica extract and panthenol (vitamin B5) can inhibit the release of inflammatory factors, reduce sensitivity, and create a stable environment for repair.
- Promote Regeneration and Repair
Ingredients such as peptides and collagen can stimulate keratinocyte proliferation and accelerate skin barrier renewal. Light therapy (such as LED red light) or radiofrequency treatments can also indirectly enhance the skin's self-repair ability by gently stimulating the dermis.
Ice Crystal Beauty primarily uses cryogenic technology to act on the skin, achieving soothing and calming effects, constricting blood vessels, reducing redness, and controlling oiliness. It is often used for post-operative care or daily skincare, quickly relieving skin discomfort while also helping to improve skin texture. Snow sensitivity is a skincare-related concept that typically refers to increased skin sensitivity to stimuli in low temperatures or cold environments. Snow sensitivity may be related to cold-induced vasoconstriction and increased sensitivity of nerve endings, manifesting as redness, tingling, or discomfort in the skin. People may experience snow sensitivity in winter or cold environments. This phenomenon is unrelated to botulinum toxin and has a completely different mechanism of action. Management of snow sensitivity typically involves moisturizing, gentle skincare, and avoiding extreme temperature changes.