Microcurrent Facials Are Replacing Botox for Many Millennials
Botulinum toxin is a highly effective biologic approved for a variety of medical and cosmetic uses, available in a variety of formulations worldwide. However, all currently approved products are administered via injection, using a conventional hypodermic needle. The injection process can be uncomfortable, such as pain, bleeding, or bruising. Therefore, developing a topical delivery method is very promising.
Botulinum toxin is a highly effective biologic approved for a variety of medical and cosmetic uses, available in a variety of formulations worldwide. However, all currently approved products are administered via injection, using a conventional hypodermic needle. The injection process can be uncomfortable, such as pain, bleeding, or bruising. Therefore, developing a topical delivery method is very promising.
Topical botulinum toxin products and microcurrent products have recently become available.
Does this mean that traditional botulinum toxin injections will gradually become obsolete?
Microcurrent generally does not allow for rapid absorption of botulinum toxin

Botulinum toxin is a bacterial exotoxin produced by Clostridium botulinum during its reproduction process. It can be used in medicine and cosmetics. Botulinum toxin can block nerve impulses between nerves and muscles, thereby relaxing overcontracted small muscles, achieving localized muscle slimming and wrinkle reduction. Microcurrent can promote blood circulation, but generally does not allow for rapid absorption of the botulinum toxin. After injection into the muscle, botulinum toxin is generally metabolized slowly out of the body over a period of approximately six months. After the injection of botulinum toxin, it is important to avoid applying heat to the area. Heat can spread the toxin to nearby muscles, reducing its effectiveness and potentially affecting nearby muscles, leading to gradual atrophy and other adverse consequences.
The Effects of Microcurrent Beauty Devices on Facial Muscles
Repetitive movements cause changes in the muscles and fascia system
These underlying issues can lead to slowed blood circulation and stiff fascia. Facial muscle problems are often overlooked, leading to aging, deformation, and even health problems.
☑️Microcurrent acts like "fascial yoga" for the muscles, releasing residual "bad tension," relaxing stiff muscles and tightening slack muscles.
☑️At the same time, the condition of the fascia is substantially improved, increasing its hydration and fluidity. This facilitates nutrient transport within cells and waste removal outside of them, boosting cell activity, accelerating metabolic rate, and promoting collagen and elastin synthesis.

Disadvantages of Injectable Administration
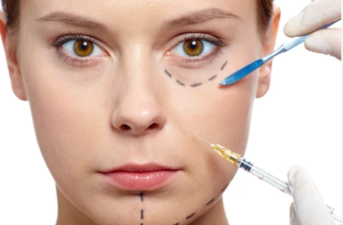
- Botulinum toxin injections have numerous drawbacks. First, the injection process can be significantly painful, especially in areas with dense nerve endings, such as the face. Second, localized skin swelling can occur after the injection, which not only affects appearance but can also cause tightness and discomfort. Injections can also cause bleeding and bruising, symptoms that can make patients reluctant to appear in public for a period of time after treatment and even require time off work. Injection administration also carries certain safety risks, such as needle misplacement, which can lead to localized off-target side effects, such as ptosis. Furthermore, botulinum toxin injections can cause systemic side effects, which, while rare, can be serious.
- Botulinum toxin injections typically require multiple injections to cover the entire treatment area. More injections increase patient discomfort and treatment time. For example, cosmetic treatments of the lower face and neck may require dozens of injections, while treatments for conditions such as hyperhidrosis and chronic migraines may require 30 or more injections. Treatment discomfort can also be affected by the sensitivity of the injection area. For example, the perioral area is often more sensitive than the forehead, making injections in these areas more painful.
- Most botulinum toxin injectable products currently on the market require reconstitution with a diluent prior to administration, a time-consuming process that could be more effectively used to provide patient care. Once reconstituted, botulinum toxin injectable products have a limited safe shelf life, potentially leading to product waste if not used promptly. If botulinum toxin injections are performed by physicians rather than nurses, the costs associated with these trained practitioners may also increase.